Dubininaís (1982) monograph is based on a detailed anatomical and histological examination of the various species, which permits, for example, the distinction of a simple seminal receptacle and an accessory seminal receptacle. The key presented here is therefore based on Dubinina (1982), although it was strongly modified taking into account my own studies as well as the keys of Gibson (1994) and Bandoni and Brooks (1987).
Dubinina (1982) recognized four families, the Amphilinidae with two subfamilies, the Amphilininae (genus Amphilina) and Gephyrolininae (genus Gephyrolina), the Schizochoeridae (genera Schizochoerus and Nesolecithus), the Austramphilinidae (genus Austramphilina), and the Gigantolinidae (genus Gigantolina). Gibson (1994) distinguished two families, the Amphilinidae and Schizochoeridae, the former including the genus Amphilina, the latter the two subfamilies Schizochoerinae (genera Gephyrolina, Nesolecithus and Schizochoerus) and Austramphilinae (genera Austramphilina and Gigantolina). Differences between species of the families appear to be very slight. Furthermore, an egg stalk is found in genera included by Gibson in two families, i.e., in Amphilina and Gephyrolina (but in none of the others). Hence only a single family, Amphilinidae, is recognized here. Bandoni and Brooks (1987) synonymized Austramphilina with Gigantolina, and Nesolecithus and Gephyrolina with Schizochoerus. Further studies, particularly of the excretory system, egg and early cleavage, are necessary to justify these synonymizations, particularly in view of the fact that a polar egg stalk is present only in Amphilina and Gephyrolina, but not in any of the other genera, and that there are significant differences in the structure of the reproductive system of Austramphilina and Gigantolina. For a list of synonyms of the genus and species names used in the following see Synonyms.
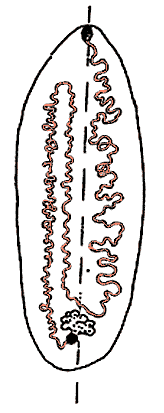
1. Eggs with stalk at one pole. Vagina with simple seminal
receptacle opening into terminal part of oviduct in front of
its opening into the ootype. The first ascending and the
descending coils of the N-shaped uterus located on one side
of the body, the second ascending coil located on the other
(Figure 1).
.............................................................2
|
|
Figure 1. Arrangement of uterine coils (red) in species of Amphilina. Note location of first ascending and descending coils to one side of midline, and of second ascending coil to the other. Redrawn from Dubinina (1982), copyright © 1982 Nauka Publishers. |
1'. Eggs lack a polar stalk. Vagina, in addition to a seminal
receptacle, possesses a large accessory seminal receptacle
(except for Austramphilina which has an undivided
seminal receptacle). Uterus of different shape. .............4
2(1). Body shape oval leaf-like. Proboscis relatively weakly developed, without specialized musculature. Testes distributed in lateral fields extending between uterine coils. Unpaired vitelline duct ascending. Ovary deeply lobed, fan-like. Excretory system reticular, without longitudinal excretory ducts. Parasites of holarctic sturgeons (Acipenseridae). ......................3 (Amphilina) 2'. Body elongate, proboscis strongly developed, with specialized radial musculature. Testes located directly on sperm ducts, lateral to uterine coils. Unpaired vitelline duct descending. Deeply lobed ovary of irregular elongate shape. Excretory system with two longitudinal lateral ducts. Parasites of siluroid fishes in India. ......................................Gephyrolina paragonopora
3(2). Testes irregularly distributed between uterine coils. External opening of vagina some distance lateral to the terminal male gonopore. Vagina crosses male duct at the level of the terminal part of the sperm duct, anterior to the ejaculatory bulb. Parasite of palearctic sturgeons. ............................................Amphilina foliacea 3'. Testes concentrated in the lateral fields of the body, lateral to uterine coils, only a few extending between the coils near posterior end of body. External vaginal opens directly beside the terminally located male pore. Vagina crosses male gonoduct at the level of ejaculatory duct, posterior to ejaculatory bulb. Parasite of sturgeons of the Amur region, Japan and North America. ......Amphilina japonica
4(1'). First ascending and descending coils of N-shaped uterus symmetrically arranged on both sides of the body relative to midline, terminal ascending part located lateral to descending part. Accessory seminal receptacle tube-like. Distal part of vagina branches and opens to the outside through one ventral and one dorsal pore. ....................5 4'. First ascending and descending coils of uterus located symmetrically on both sides of the body relative to midline, second ascending coil between them. Accessory seminal receptacle sac-like. Distal part of vagina opens to the outside through single pore. ................................7
5(4). Body elongate, leaf-like. Accessory seminal receptacle reaches approximately 1/3 body length. .....................................Schizochoerus liguloideus 5'. Body oval leaf-like. Accessory seminal receptacle reaches approximately 1/6 body length. ...............6 (Nesolecithus)
6(5'). Vitelline glands extend further anteriorly than testes. Accessory seminal receptacle without narrow basal part, of equal width along its whole length. Vagina short, its length from distal branching to accessory seminal receptacle equal to diameter of ovary. Parasite in body cavity of Arapaima gigas (Clupeiformes) in the Amazon. .........................................Nesolecithus janickii 6'. Testes extend further anteriorly than vitelline glands. Accessory seminal receptacle with basal narrow and distal swollen part. Vagina elongate, several times longer than diameter of ovary. Parasite in body cavity of Gymnarchus niloticus (Mormyriformes) in West Africa (Nigeria). .......................................Nesolecithus africanus
7(4'). Joint external opening of vagina and male gonoduct (common gonopore). Ovary not lobed, irregularly bean-shaped, lateral to anterior part of accessory seminal receptacle. Frontal glands consist of many cells and are restricted to anterior end of body, single ducts open directly at level of proboscis. Eggs ellipsoid. ............Austramphilina elongata 7'. External opening of vagina dorsal, short distance in front of terminal male gonopore. Ovary deeply lobed, with two wings, medial, posterior to accessory seminal receptacle. Frontal gland cells concentrated around a common duct which begins at anterior margin of accessory seminal receptacle and opens anteriorly in apical deepening. Eggs spherical. .............................................Gigantolina magna



 Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site
Go to quick links
Go to quick search
Go to navigation for this section of the ToL site
Go to detailed links for the ToL site